The 6.6L Duramax LB7 was the first engine produced in the Duramax 6600 family. It was designed and developed by DMAX, a partnership forged between General Motors and Isuzu Motors Ltd, a prominent vehicle and diesel engine manufacturer based out of Japan. At the time of the formation of DMAX, Isuzu had already been providing GM with support in the commercial vehicle sector, primarily in the form of GM branded Isuzu cab-over trucks. At the time, Isuzu's track record in producing reliable diesel engines was significantly greater than GM's. Knowing full well the shortcomings of the outgoing 6.5L turbodiesel, GM sought to produce an engine that would provide them with a competitive edge moving forward; with the help of Isuzu, GM undoubtedly succeeded in their endeavor and one of the most successful diesel engine platforms was created in record time.
The 6.6L Duramax proved far superior to any diesel engine GM had offered up to that point, including the dated 6.5L Detroit platform. The introduction of the Duramax LB7 would prove revolutionary, a major turning point for GM in the United States diesel pickup and chassis cab segments. GM employed a heavy duty Allison 1000 five speed automatic transmission to manage the new engine's power, which proved to be a winning combination. A ZF six speed manual transmission was also offered mated to the 6.6L Duramax, however the Allison 1000 was far more popular by a wide margin.
The 6.6L Duramax featured an exclusive common rail injection system, which its closest competitors would not adopt until a future date (the 5.9L Cummins became a common rail for the 2003 model year, while Ford would not offer its first common rail until the 2008 model year). At just north of 400 cubic inches, the engine's 6.6 liter displacement offered a favorable balance between fuel economy potential and overall performance. With nearly a 1 to 1 bore-to-stroke ratio, the architecture of the engine provides generous mid-range power without sacrificing low end torque.
In addition to the Chevrolet Silverado and GMC Sierra, the new engine platform found its way into GM's medium duty truck line and was available in the GMC TopKick and Chevrolet Kodiak. Problems with LB7 fuel injectors were quickly identified as dealerships became flooded with repair orders for failed injectors. The root cause of the issue would later be determined to be the location of the fuel injectors beneath the valve covers. Injector failures became so common that GM was forced to issue a recall, replace them with an updated design, and assure their loyal customer base that the problem was eliminated by extending the warranty on fuel injectors through 200,000 miles. Despite these early injector failures, the 6.6L Duramax was featured in Ward's "10 Best Engines" list for the 2001 and 2002 model years. The LB7 would run its course into the 2004 model year when a redesigned Duramax diesel, the LLY, began replacing it mid-model year.
6.6L LB7 Duramax Engine Specs
| Engine Family | 6.6L Duramax diesel (Duramax 6600) | |
| RPO Code | LB7 | |
| VIN Code | 1 (8th digit of VIN) | |
| Assembly Site | DMAX engine plant, Moraine, Ohio | |
| Applications/Production Years | 2001 - 2004 Chevrolet Silverado 2500, 3500 2001 - 2004 GMC Sierra 2500, 3500 2003 - 2004 Chevrolet Kodiak C4500, C5500 2003 - 2004 GMC TopKick C4500, C500 |
|
| Displacement | 6.599 liters (6.6 liters nominal), 402.62 CID (403 CID nominal) | |
| Configuration | 90 degree V-8 | |
| B10 Life | Not specified | |
| B50 Life | Not specified | |
| Bore | 4.055 inches (103.00 mm) | |
| Stroke | 3.897 inches (99.00 mm) | |
| Bore/Stroke Ratio | 1.04 (marginally oversquare) | |
| Compression Ratio | 17.5 : 1 | |
| Firing Order | 1-2-7-8-4-5-6-3 | |
| Cylinder Numbers |  Cylinders 1, 3, 5, and 7 are located on the passenger side bank Cylinders 2, 4, 6, and 8 are located on the driver side bank |
|
| Engine Block Material | Cast gray iron, induction hardened, deep skirt engine block | |
| Cylinder Head Material | Cast aluminum alloy | |
| Injection System | Direct injection Bosch high pressure common rail system, piezoelectric fuel injectors Bosch CP3 (CP3.3) injection pump 23,000 psi max injection pressure |
|
| Aspiration | Turbocharged, intercooled (air-to-air intercooler/charge air cooler) IHI RHG6 turbocharger, wastegated |
|
| Minimum Cylinder Pressure | 300 psi (minimum compression test pressure) | |
| Reciprocating Assembly | Fracture split forged alloy steel connecting rods Nitrided forged steel crankshaft Forged steel camshaft Cast iron main bearing caps |
|
| Valvetrain | Overhead valve (OHV), standard cam-in-block, mechanical roller lifters 4 valves per cylinder (32 valve) |
|
| Cold Start Aid(s) | Traditional glow plug system, 1 per cylinder | |
| Engine Oil Capacity | 10 quarts with oil filter change | |
| Engine Oil Spec | See viscosity chart at 6.6L Duramax LB7 service guide | |
| Lube Oil Filter P/N | ACDelco PF2232 | |
| Fuel [1] | #2 low sulfur diesel fuel preferred (includes winterized blends) #1 low sulfur diesel fuel acceptable in cold weather Not certified by OEM for use of biodiesel or biodiesel blends |
|
| Horsepower | Standard | 300 hp @ 3,100 rpm |
| Kodiak/TopKick LRY | 210 hp @ 2,750 rpm | |
| Torque | Standard | 520 lb-ft @ 1,800 rpm |
| Kodiak/TopKick LRY | 520 lb-ft @ 1,600 rpm | |
| Idle Speed | ~ 680 rpm @ operating temperature | |
| Governed Speed | ~ 3,400 rpm (electronically governed) | |
| Emissions Equipment | Exhaust gas recirculation (w/ CA emissions) | |
| Coupled Transmissions | Allison 1000 5 speed automatic, ZF S6-650 6 speed manual | |
| Engine Weight | Approx. 835 lbs | |
| Engine Dimensions | Length | Approx 30.0 inches |
| Width | Approx 30.0 inches | |
| Height | Approx 32.0 inches | |
[1] - Ultra low sulfur diesel (ULSD) supersedes low sulfur diesel (LSD) specification in the United States, original OE recommendations listed.
6.6L LB7 Duramax Horsepower & Torque Curves
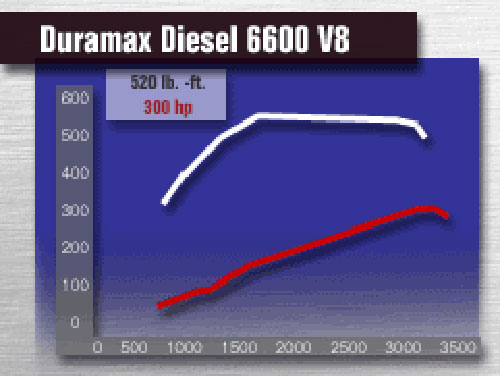
Source - GM Powertrain Division, 2001

Editor, Diesel Hub
