The Detroit 60 Series engine platform was unique in many ways. First and foremost, Detroit essentially pioneered the electronically controlled diesel engine segment with it's 1987 model year 60 Series. This drive-by-wire system relied on an electronic control module (ECM) and injector driver module in order to actuate electric solenoids on each individual fuel injector. This system paved the way for superior injection control, thus maximizing fuel economy and performance in addition to granting the vehicle various diagnostic features and reduced emissions.
Furthermore, the Detroit 60 Series features a single overhead camshaft to operate its intake valves, exhaust valves, and fuel injector plungers. One could argue that the Detroit 60 Series was somewhat ahead of its time, but it did not suffer reliability/longevity concerns often associated with new, unproven concepts.
Detroit 60 Series Engine Specs
| 11.1L Detroit 60 Series | 12.7L Detroit 60 Series | 14.0L Detroit 60 Series | |
| Manufacturer | Detroit Diesel | ||
| Applications | 1987 - 1997, various on/off highway | 1987 - 2007, various on/off highway | 2001 - 2011, various on/off highway |
| Engine Type | 4 cycle turbodiesel, wet cylinder liners | ||
| Configuration | Inline 6 cylinder | ||
| Displacement | 677 CID, 11.1 liters | 778 CID, 12.7 liters | 858 CID, 14.0 liters |
| Firing Order | 1 - 5 - 3 - 6 - 2 - 4 | ||
| Engine Block | Cast iron, wet cylinder liners, 7 main bearings | ||
| Cylinder Head | Cast iron, overhead cam | ||
| Compression Ratio | 16.0:1 | 15.0:1 or 16.5:1 | 15.0:1 or 16.5:1 |
| Cylinder Bore | 5.12 inches (130 mm) | 5.12 inches (130 mm) | 5.24 inches (133 mm) |
| Cylinder Stroke | 5.47 inches (139 mm) | 6.30 inches (160 mm) | 6.62 inches (168 mm) |
| Valvetrain | Overhead camshaft, roller follower rocker arms, 4 valves per cylinder (2 intake, 2 exhaust valves per cylinder) | ||
| Injection | Electronically controlled EUI (electronic unit injector) injection system (see DDEC section below) | ||
| Aspiration | Turbocharged, air-to-air intercooler | ||
| Engine Dimensions (approx.) | Length - 57 inches | ||
| Width - 34 inches | |||
| Height - 50 inches | |||
| Engine Weight (approx) | 2,675 lbs | 2,800 lbs | 2,800 lbs |
| Horsepower | 250 - 350 hp @ 1,800 rpm | 380 - 455 hp @ 1,800 rpm | 425 - 515 hp @ 1,800 rpm |
| Torque | 1,100 - 1,250 lb-ft @ 1,200 rpm | 1,350 - 1,550 lb-ft @ 1,200 rpm | 1,550 - 1,650 lb-ft @ 1,200 rpm |
| Max Engine Speed | 2,100 rpm (some continuous duty applications may be governed at 1,800 rpm) | ||
An improved engine block was introduced after November 30th, 1994; engines with serial number 6R210293 and later feature this engine block design. A more significant engine block improvement was introduced May 2nd, 1998 and is found in engines with serial number 6R408505 and later. This new design introduced a new lubrication circuit which granted the use of piston cooling jets.
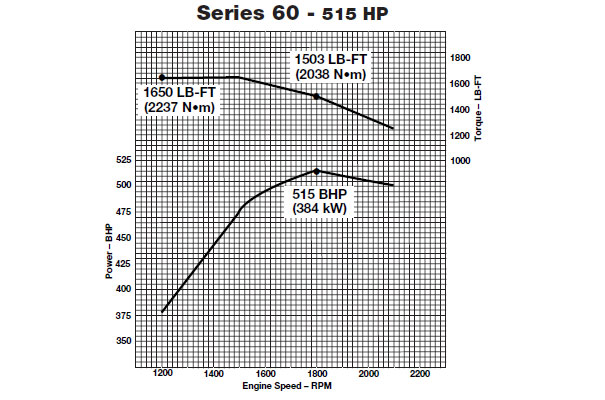
Detroit 60 Series Horsepower and Torque Curves
DDEC Injection Control
The Detroit 60 Series engine family uses EUI (electronic unit injector) fuel injectors that are operated by the ECM (engine control module). The ECM processes various sensor inputs and uses this information to control injector timing, pulse width (amount of fuel injected per injection event), and injection pump pressure (injector feed pressure). The system is called Detroit Diesel Electronic Control, or DDEC for short. The DDEC system was updated several times over the course of the 60 Series' production.
DDECI - The first generation DDEC system used an Electronic Distributor Unit (EDU) to actuate the injector solenoids. Injection events are commanded by the ECM, but physically carried out by the EDU.
DDECII - The second generation DDEC system eliminated the EDU and instead the ECM picked up the task of actuating the injector solenoids. This simplified the engines computer system and may have provided improved reliability and diagnostic functions.
DDECIII & DDECIV - Third and fourth generation DDEC systems expanded diagnostic capabilities and introduced the Diagnostic Data Reader (DDR) function.
Each change of the DDEC system represented an improvement in emissions and diagnostic capabilities, amongst other features. The DDEC also has the ability to shut an engine down in the event of an emergency that may result in severe engine damage, such as low/no oil pressure, excessive engine coolant temperature, and excessive oil temperature.
The EUI injectors are unique in that they have the inherent properties of both an electronic and mechanical unit injector. While an injection pump provides pressurized fuel to each individual injector it is a camshaft driven plunger that produces the final injection pressure. Meanwhile, injection events are initiated by ECM controlled electric solenoids.
Detroit 60 Series Model Number Breakdown
The engine model number is an 8 digit code stamped on the engine block in the vicinity of the engine serial number (production/build number). The values correspond to the following options/information:
| Digit(s) | Value(s) | Indication |
| 1 | 6 | 60 Series engine family |
| 2 & 3 | 06 | Six cylinder engine |
| 4 | 2 | Marine application |
| 3 | Industrial application | |
| 5 | Generator application | |
| 7 | On-highway truck application | |
| 5 | W,S,E, or L | 11.1L engine |
| G,T, or M | 12.7L engine (standard version) | |
| P or B | 12.7L engine (heavy duty/premium version) | |
| F or H | 14.0L engine | |
| 6 | T | DDECI (1st generation DDEC) |
| U | DDECII (2nd generation DDEC) | |
| K | DDECIII or DDECIV (3rd or 4th generation DDEC) | |
| 7 & 8 | 28 | 1991+ model year coach application |
| 32 | Underground mining application | |
| 40 | Pre-1991 model year engine | |
| 60 | 1991+ model year on-highway truck application |
