DT466 Model Year Changes, Variations, and Design Progressions
1984 to 1995 models featured a mechanical injection system. More specifically, the 1984 to 1992 DT466 employed a Bosch MW injection pump, while 1993 to 1995 models featured a Bosch P pump. All 1996 to current models used an HEUI (hydraulically actuated electronically controlled unit injector) fuel system. The P pump DT466 was actually used in select applications through the 1997 model year, but these are uncommon. Likewise, the HEUI injection system was first introduced for 1994, although these engines coexisted with mechanically injected engines for several years.
In 2004, International Navistar introduced the EVRT (electronic variable response turbocharger), a type of variable geometry turbocharger (VGT) that controlled and adjusted turbocharger A/R per operating conditions in order to reduce lag and improve overall performance. For 2010, a twin sequential turbocharger system was employed for further improvements in throttle response, overall performance, and reduced emissions. All engines 2003 and prior featured a standard fixed geometry turbocharger. Early engines featured a 2 valve per cylinder head design, while HEUI models were upgraded to a 4 valve per cylinder head design for favorable airflow characteristics.
Beginning in 2007, the DT466 namesake was retired in favor of International's new emissions compliant engine family designation and the engine was renamed the MaxxForce DT - the current model engine continues to use this name.
Keep in mind that there will be certain exceptions and the possibility that certain model year engines were carried over despite the launch of an improved product, therefore the aforementioned dates may not apply entirely to every application.
DT466 (MaxxForce DT) Specs
| Manufacturer | International Navistar (formerly International Harvester) |
| Name | MaxxForce DT (formerly DT466) |
| Displacement | 7.6 liters, 466 cubic inches |
| Block | Cast Iron, wet sleeve, inline 6 |
| Bore | 4.59 inches |
| Stroke | 4.68 inches |
| Firing Order | 1-5-3-6-2-4 |
| Compression Ratio | 16.4 : 1 (compression ratio may vary by application) |
| Aspiration | Turbocharged & intercooled in various configurations through the years, including a sequential twin turbo system. |
| Injection | Direct injection • 1984 - 1995: Mechanical injection pump • 1994 - 2004: HEUI injection system • 2004 - present: Generation 2 HEUI injection system |
| Horsepower | Up to 300 hp @ 2,200 rpm |
| Torque | Up to 860 lb-ft @ 1,300 rpm |
| Engine Weight | 1,425 lbs dry |
| B50 Engine Life | 550,000 miles |
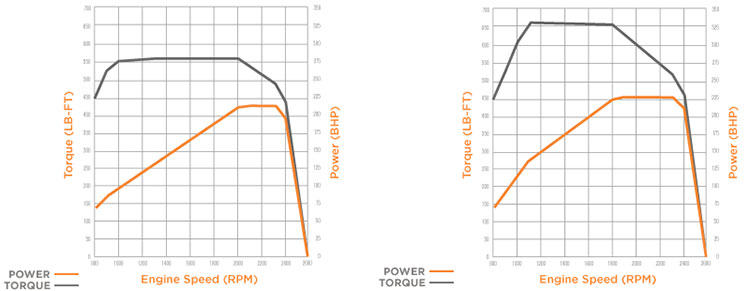
The horsepower/torque curves above correspond with two DT466 (MaxxForce DT) ratings available for 2016.
The wet cylinder sleeve design allows for less downtime and reduced repair costs - under many circumstances, an engine overhaul can be performed without removing the engine from a chassis. Additionally, it has been suggested that a wet sleeve cylinder provides greater durability in comparison to a dry sleeve system. The DT466 generates torque at a favorably low 1,300 rpm and the latest model has a governed speed of 2,400 rpm. Modern versions of the engine prove that the HEUI injection system is sophisticated enough to cope with strict emissions control requirements in the United States, although the consensus is that this mode of injection is seemingly outdated since widespread adoption of high pressure common rail technology.
